Polyisocyanide hydrogels with tunable nonlinear elasticity mediate liver carcinoma cell functional response
Available online 16 June 2022
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma development is closely related to the changes in tissue mechanics induced by excess collagen deposition and crosslinking, which leads to liver fibrosis and malignant progression. The role of matrix stiffness has been widely assessed using various linearly elastic materials. However, the liver, like many soft tissues, also exhibits nonlinear elasticity by strain-stiffening, allowing cells to mechanically interact with their micromilieus which has attracted much attention in cellular processes recently. Here, we use a biomimetic hydrogel grafting of GRGDS peptide with tunable nonlinear mechanical properties, polyisocyanides (PIC), to investigate the influence of strain-stiffening on HepG2 liver cancer cell behavior by tuning PIC polymer length. Compared to short PIC polymer with lower critical stress, PIC hydrogels composed of long polymer with higher critical stress promote the motility and invasiveness of HepG2 cells, and induce more actin stress fibers and higher expression level of mechanotransducer YAP and its nuclear translocation. Strikingly, the expression of calcium-activated potassium channel KCa3.1, an important biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma, is also affected by the mechanical property of PIC hydrogels. It was also shown that downregulating the KCa3.1 channel can be achieved by inhibiting the formation of actin fibers. Our findings imply that the strain-stiffening property of PIC hydrogels affects the expression of KCa3.1 potassium channel via mediating cytoskeletal stress fiber formation, and ultimately influences the liver carcinoma cell functional response.
Material and Methods
Laser holography analysis
First, HepG2 cells were seeded in PIC hydrogels in a 24-well plate and cultured for 7 days to generate the cell behavior changes induced by different matrix mechanical properties, and then the cells were recycled by low-temperature centrifugation and reseeded on different PIC hydrogels correspondingly. After that, a laser holographic imaging system (Phiab, M4) instrument was employed to continuously image the traces of individual cells in the three groups (P1, P2, and P3) for 24 h every 0.5 h (three replicates per group and three observation areas per well). Single-cell tracking was performed by the "HoloMonitor" software, which can select and track cells and their positions in each frame. The data were analyzed through "HoloMonitor" software to obtain the average migration speed and migration distance of cells.
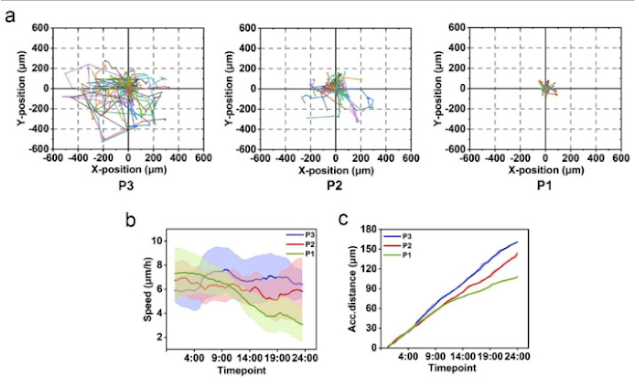
Influence of mechanical property on HepG2 cell mobility
We further investigated the influence of mechanical properties of PIC hydrogels on HepG2 cell mobility. This was done with phase holographic microscopy where 24 h long time-lapse movies of cells on PIC hydrogels were acquired. For each cell, the center of mass was determined and monitored over time. In Fig. 6a, rose plots are used to display single-cell trajectories, showing the cell migration behavior after stimulated by different PIC hydrogels for 7 days. The velocity (Fig. 6b) and accumulated distance average (Fig. 6c) of the migration patterns were further quantified. We observed that P3 matrix with higher critical stress and stiffer mechanical properties promotes the mobility behavior of HepG2 cells characterized by faster migration speed, longer migration distance, and larger migration range. However, HepG2 cells demonstrated similar migration patterns and distance in the control group of P2-1, P2, and P2-4 hydrogels (Fig. S11 in supporting information).
Fig. 6. The mobility of HepG2 cells after encapsulated in PIC hydrogels for 7 days. The migration trajectory (a), average migration rate (b), and accumulated distance (c) of HepG2 cells within 24 h after encapsulated in different PIC hydrogels for 7 days. The standard deviation is represented as a shaded area for each line.
Abstract 5327: Characterization of a green, temperature activated nano formulation that drives the mechanism of doxorubicin toxicity from apoptosis to ferroptosis
June 15 2022
Abstract
Introduction: Nano formulations continue to be a very attractive venue for the development of “smart” drug delivery systems. Emerging green (organic) formulations do not require harsh chemical solvents and are easy to prepare.
Solid Core Lipid Formulations: The lipid phase (l.p.) contained a solid fatty acid (lauric acid) and liquid lipid (oleic acid) with or without Doxorubicin. 55° surfactant containing an emulsifying agent (Brij-58) mixed with nonionic surfactant (Span 80) was dropwise added. The emulsion was cooled to form temperature-activated nanoparticles (TAN). Before usage, the emulsion was activated by heating to 41°C.
Experiments: B16F10 melanoma, U87-MR glioblastoma, MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines were analyzed on a variety of quantitative Imaging platforms.
Results iCyte (CompuCyte): Laser based instrument for obtaining quantitative fluorescence and light scatter measurements. We obtained single endpoint dosage response curves to compare the TAN with free Dox, and found the TANs were effective at 4-6 times lower equivalent Dox concentrations.
Holomonitor (Phase Holographic Imaging): The HM4 resides in tissue culture incubators and allows long-term medium resolution holographic imaging. It offers a complete image processing library including routines for proliferation and cell tracking. We devised methods for 4-dimensional imaging (X pos. vs. Y pos. vs Time, vs. Density). Thus, we are able to monitor the temporal effects of the compounds.
Cell Explorer (Nanolive): The Cell Explorer has a a rotating mirror that directs the laser in an orbit around the sample to obtain super-resolution 3D tomographs. It enables long-term time-lapse imaging via stage-top environmental chamber. It is well suited for quantifying sub cellular components such as mitochondria and lipids. HT-2 (Tomocube): The HT-2 is a label-free ultra-high resolution holotomography system complemented by fluorescence capabilities. Combined RI and fluorescence images give the highest information content of any of the platforms.
Discussion: In 2012, Dixon et al described ferroptosis as a distinct new form of cell death through the iron dependent accumulation of oxidatively damaged phospholipids. They state that a diagnostic feature is mitochondrial shrinkage and collapse. We confirmed this in our tomographic imaging images. Other features that were detected and consistent with ferroptosis are loss of nuclear contents, a thickening of the nuclear membrane, and peri-nuclear mitochondrial accumulation. In 48-hour HM4 plots control cells show numerous mitotic events. Dox treated cells show cellular enlargement but no mitotic events. In the TAN population at about 20 hours, there is sudden death occurring in the entire population.
Conclusion: Our experiments suggest a high potency of the newly developed TANs. Ferroptosis is the most likely mechanism of action.
Mvh the99
Som service till alla ev HoloMonitornyfikna forskare : PHIAB Webshop


thank you for nice information, finally found what am I looking for!!!
SvaraRaderavisit our website : muhammad solehuddin