Quantitative Phase Imaging for Label-Free Analysis of Cancer Cells—Focus on Digital Holographic Microscopy
Abstract
To understand complex biological processes, scientists must gain insight into the function of individual living cells. In contrast to the imaging of fixed cells, where a single snapshot of the cell’s life is retrieved, live-cell imaging allows investigation of the dynamic processes underlying the function and morphology of cells.
Label-free imaging of living cells is advantageous since it is used without fluorescent probes and maintains an appropriate environment for cellular behavior, otherwise leading to phototoxicity and photo bleaching.
Quantitative phase imaging (QPI) is an ideal method for studying live cell dynamics by providing data from noninvasive monitoring over arbitrary time scales.
The effect of drugs on migration, proliferation, and apoptosis of cancer cells are emerging fields suitable for QPI analysis.
In this review, we provide a current insight into QPI applied to cancer research.
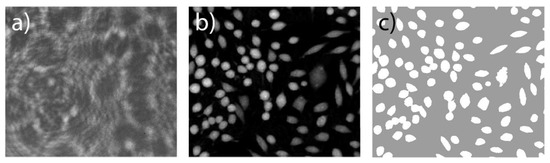
Figure 1. Example of QPI image: (a) Interference pattern from digital holography (DH) recording showing cells in transmission mode as seen by the sensor. An interference pattern between object and reference wave has been disturbed by the refraction of cells in the object light path; (b) Reconstructed phase image using a Fresnel approximation, numeric refocusing, and unwrapping. Image intensity is proportional to optical path length through the cells; (c) Reconstructed phase image with segmented cell areas. Cell regions (white) have been separated from background (grey) using a simple thresholding. Scale: 200 × 175 µm2, human prostate DU145 cells in a T25 flask.
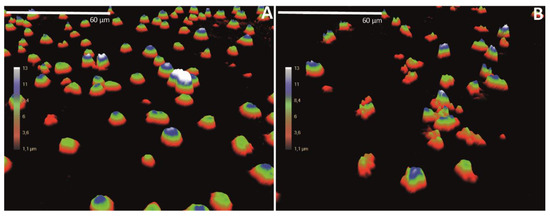
We have cultured T leukemia Jurkat cells in ibidi chambers (ibidi GmbH, Martinsried, Germany) and treated the cells for 24 h with the cell death-inducing agent etoposide, or left untreated as a negative control.
After the incubation, the cells were analyzed with DH microscopy.
3D holograms are shown for untreated cells and for the etoposide-treated cells.
Utdrag från rapporten som visar potentialen. (tänk AI i förlängningen)
In supervised machine learning, a model classification algorithm is trained using a training sample set consisting of training data labeled, classified, or annotated manually to provide a ground truth.
When training is complete, the obtained model is validated on test data of unknown class.
The more representative the training data is to the expected test data, the more accurate the classifier.
In many real-world scenarios, test data may differ significantly from the training set.
A promising potential for cellular imaging is the ability to use QPI to combine the non-invasive full-field imaging at short imaging intervals with automated analysis of spatio-temporal cell signatures, which enables the gathering of data from a large number of individual cells for long periods of time, typically several cell cycles.
QPI applications including cell counting, migration, and morphology assays have become increasingly popular, but several challenges still persist.
The morphological label-free analysis ability of QPI is a fast, automatic, and cost-efficient evaluation tool for analyzing quantitative parameters, including cell area, thickness, volume, population confluence, and cell count.
The need for QPI applications in clinical cancer diagnostics and treatments is emerging.
There is a demand for tools to classify cells, and to determine cell morphology, differentiation, proliferation, morphological changes of cells transfected with DNA or siRNA, cell death, and effects on cell movement—all in a high-throughput manner.
Since QPI is performed on live cells without any labeling, the cells can be investigated with other methods—or the cells can be cultured for longer periods after the analysis.
Inga kommentarer:
Skicka en kommentar