
BCAP31, a cancer/testis antigen-like protein, can act as a probe for non-small-cell lung cancer metastasis
Received Accepted PublishedNon-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) represents most of lung cancers, is often diagnosed at an advanced metastatic stage.
Therefore, exploring the mechanisms underlying metastasis is key to understanding the development of NSCLC. The expression of B cell receptor-associated protein 31 (BCAP31), calreticulin, glucose-regulated protein 78, and glucose-regulated protein 94 were analyzed using immunohistochemical staining of 360 NSCLC patients.
It resulted that the high-level expression of the four proteins, but particularly BCAP31, predicted inferior overall survival.
What’s more, BCAP31 was closely associated with histological grade and p53 status, which was verified by seven cohorts of NSCLC transcript microarray datasets. Then, three NSCLC cell lines were transfected to observe behavior changes BCAP31 caused, we found the fluctuation of BCAP31 significantly influenced the migration, invasion of NSCLC cells.
To identify the pathway utilized by BCAP31, Gene Set Enrichment Analysis was firstly performed, showing Akt/m-TOR/p70S6K pathway was the significant one, which was verified by immunofluorescence, kinase phosphorylation and cellular behavioral observations.
Finally, the data of label-free mass spectroscopy implied that BCAP31 plays a role in a fundamental biological process. This study provides the first demonstration of BCAP31 as a novel prognostic factor related to metastasis and suggests a new therapeutic strategy for NSCLC.
Ur forskningsrapporten klipper jag ur det PHI-relevanta.
Materials and Methods
Label-free time-lapse holographic imaging and analysis
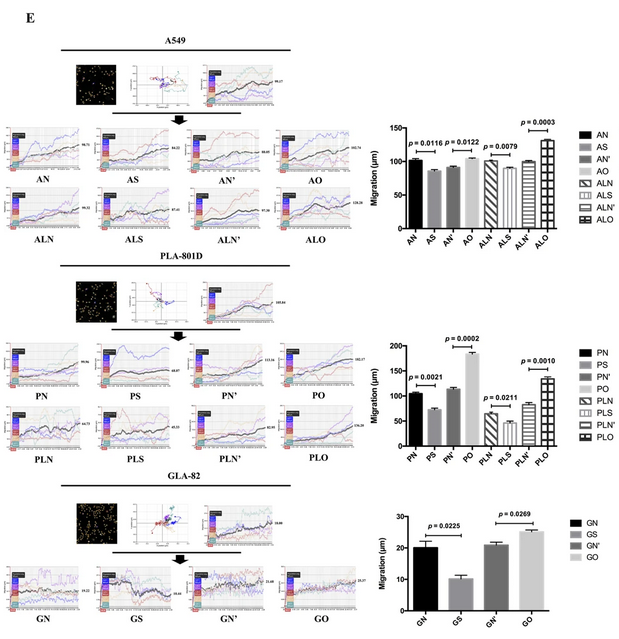
Cell morphology was studied using a label-free technique and digital holographic microscopy using a HoloMonitor M4 (Phase Holographic Imaging, Lund, Sweden). Cells were tracked for 96 h by imaging at 15 min intervals. All indices were analyzed using HoloMonitor (HoloStudio).To gain a better view of cell morphological changes, HoloMonitor M4 was used to collect real-time images of unlabeled live cells using a low-power 635 nm diode laser. After transfection, regardless of whether BCAP31 expression was up- or down-regulated, all cells showed a change in size. When BCAP31 expression was decreased, cells from some groups (A549, PLA-801D, and GLC-82) were larger than the negative control, while some cells (PLA-801D and GLC-82) were smaller than the negative control, with increased BCAP31 expression.
The migration and invasion of tumor cells mainly relies on factors such as enhanced mobility, depressed intercellular adhesion and the degradation of extracellular matrix. BCAP31 promoted NSCLC cell motility and migration in wound-healing assays, transwell assays without matrigel, and HoloMonitor M4 monitoring migration.
Both HoloMonitor M4 analysis of cell areas, and immunofluorescence staining of F-actin, showed that BCAP31 affected cell morphology and marginally promoted F-actin redistribution to the periphery, which could facilitate cell migration and invasion. STRING analysis further identified F-actin-relevant genes, including PRR5, RICTOR and MAPKAP1 (all of which are connected with MTOR), which provided further evidence of a role for the Akt/mTOR pathway in cell migration and invasion. Further interpretation of western blotting analysis and wound-healing experiments, and analysis of our previous results, appears to suggest that BCAP31 is not a member of the Akt/mTOR/p70S6K pathway, but can affect the other molecules in this critical pathway in order to influence cell migration.
Min kommentar
Jag ger mig inte på att dissikera denna studie närmare än att nämna att forskarna studerat den vanligaste formen av lungcancer, Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), och då i dess vanligaste diagnostyp via metastaser. De har gett sig på den svåra processen att förstå de mekanismer som ligger bakom denna metastasering via ett antal kroppsegna proteiner,protein 31 (BCAP31), calreticulin, glucose-regulated protein 78, and glucose-regulated protein 94.
Slutsatserna de drog sammanfattades enligt följande:
Finally, the data of label-free mass spectroscopy implied that BCAP31 plays a role in a fundamental biological process. This study provides the first demonstration of BCAP31 as a novel prognostic factor related to metastasis and suggests a new therapeutic strategy for NSCLC.
HoloMonitor ståtar ånyo med assistans till forskares helt nya kunskaper inom cancer.
Mvh the99
Ps. Tack till de 2 tipsarna Axel och Henrik som uppmärksammade bloggen på denna artikel. Ds
Inga kommentarer:
Skicka en kommentar